How to Reverse Image Search on iPhone
![]()
Reverse image search is an incredibly useful technology, allowing you to locate online photos that are an exact match or similar in some way to your own. It can also be used to search for products and places just by supplying a picture, even if it’s an image that you found online. With the right app, it’s possible to get a live result from your smartphone’s camera.
Table of Contents
Using the Google App
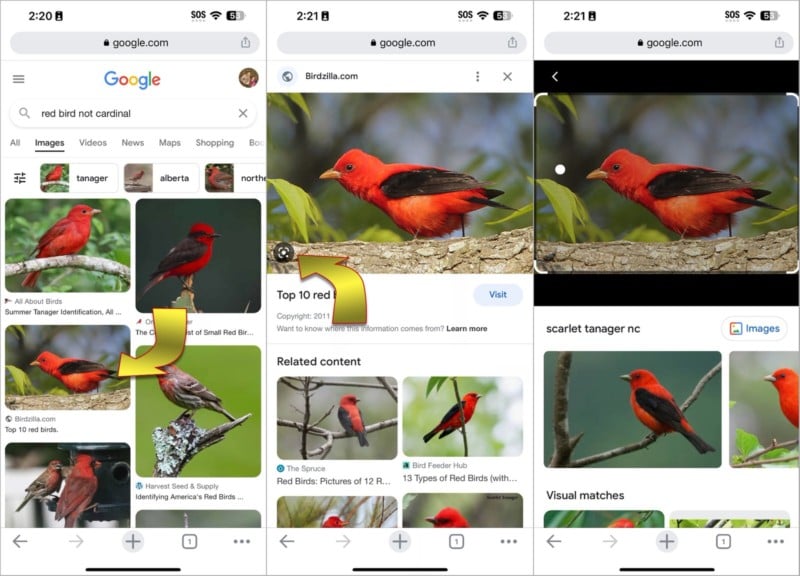
Google has the world’s most popular reverse image search and this is incorporated into its Google Lens image AI technology. You might think of this as an Android exclusive, but you can get easy access to Google Lens (and Google Assistant) on your iPhone by installing the Google app. To begin a reverse image search, open the Google app and tap the Lens icon which looks like a colorful camera in the search bar. If you have added the Google widget to your home screen, you can tap the Lens icon directly.
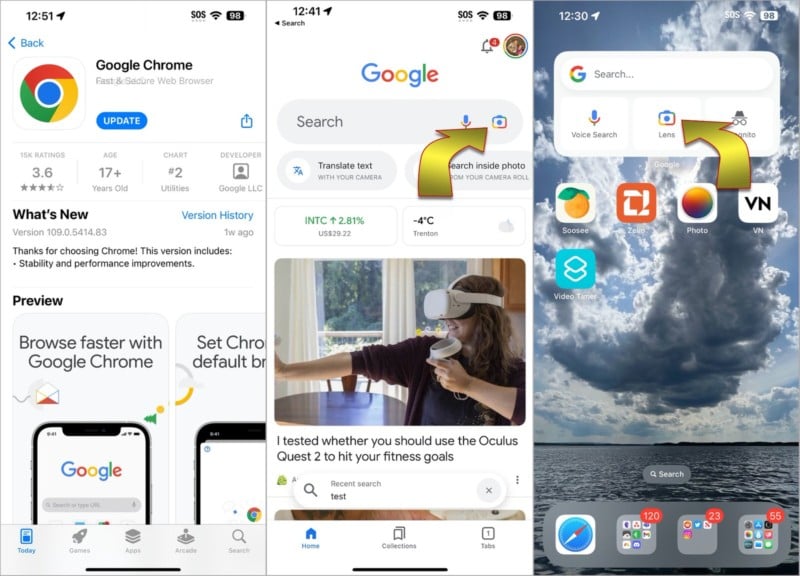
Google Lens allows you to search for anything that’s visible in your camera’s viewfinder. If the camera preview isn’t already open, tap Search with your camera, then center the item of interest and tap the shutter button. Instead of taking a photo, Google Lens will use this picture for a reverse image search.
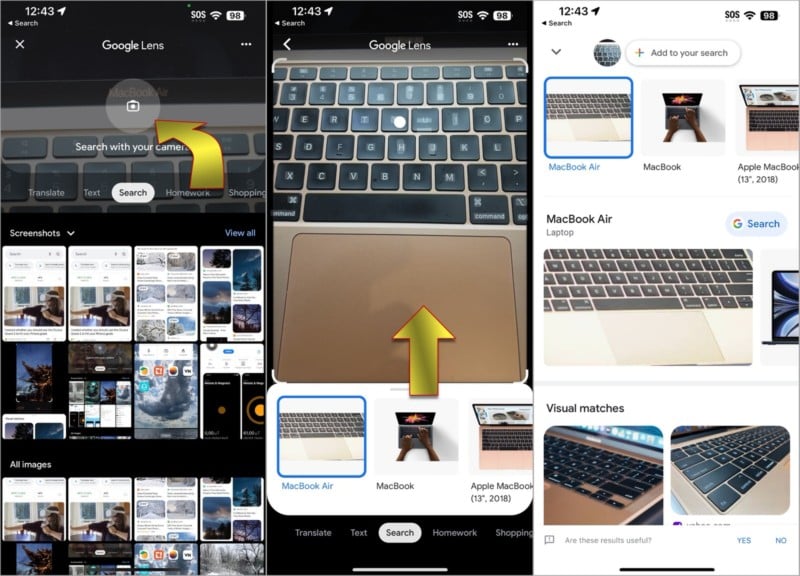
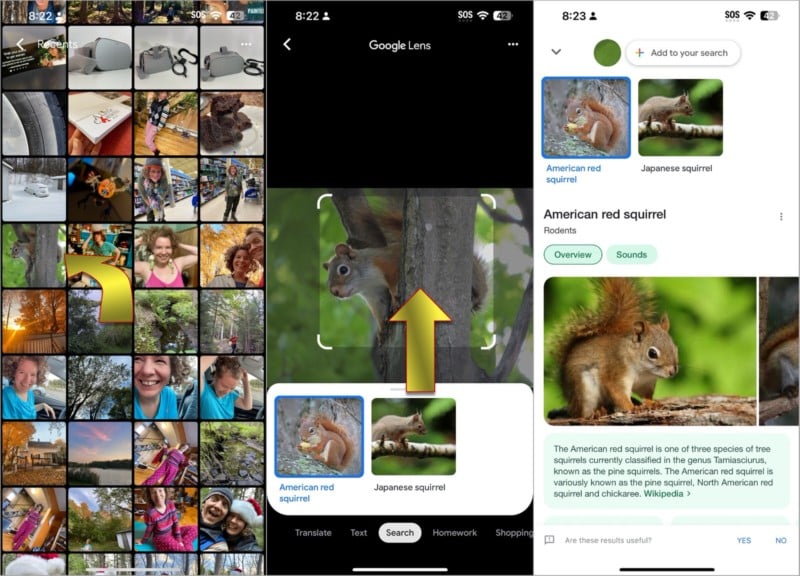
You can also choose any picture from your iPhone’s photo library for a reverse image search by picking from the images at the bottom. The Google app shows the Screenshots album, but you can select any other album, including the Recents album which includes your photos sorted by date. Tap View all to see a full-screen gallery of photos.
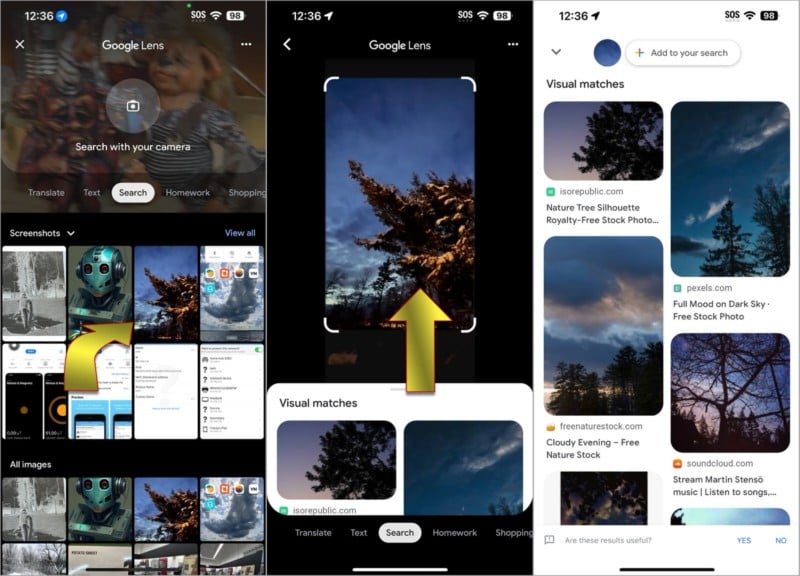
The results of the search might vary considerably. Google Lens isn’t perfect, but it’s one of the best options available for finding similar images. If you don’t find what you’re looking for, it’s possible to refine the results by typing a few words in addition to the image you supply. That can make a big difference if the images returned by a search are highly varied.
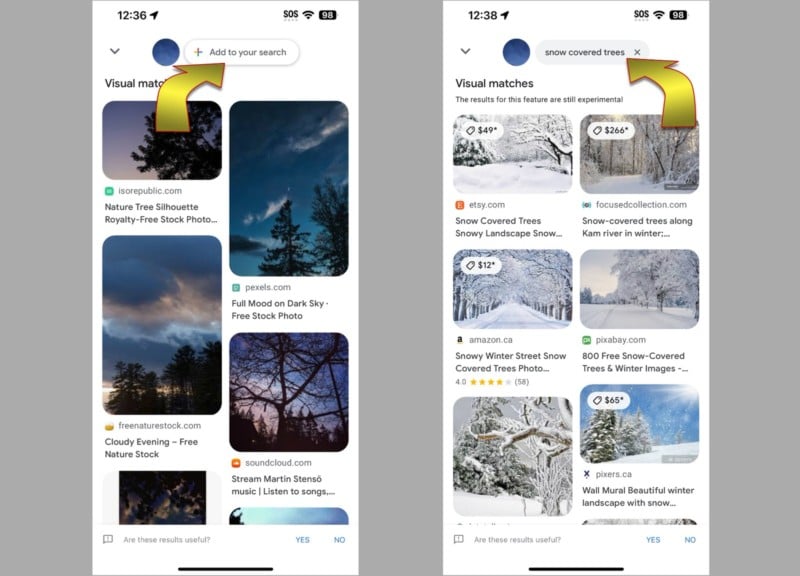
After searching for a related image, drag the bar at the top of the results upward to stretch that panel to full height. At the top, you’ll see a button labeled Add to your search. Selecting this option will open a search box that lets you add keywords to narrow in on better matches to your image.
Related Image Search with Safari
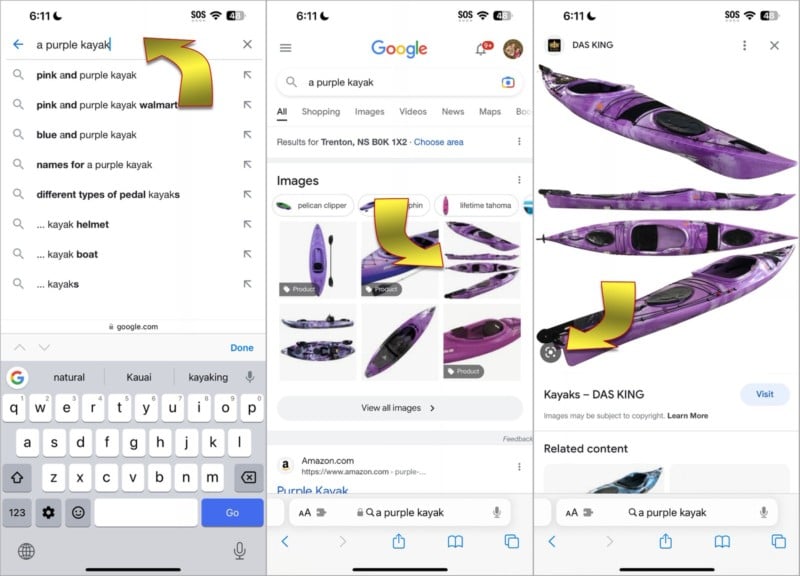
The Safari browser that comes preinstalled on your iPhone defaults to using Google when starting an internet search from the address bar and you can easily turn that into a Google Image search to find related images. You can’t, however, supply your own pictures when using this method. You can, however, start with a regular Google image search, then you can narrow the search down by tapping an image that’s close to what you want and selecting the viewfinder icon in the lower-left corner to find related images.
Using Google’s Chrome Browser
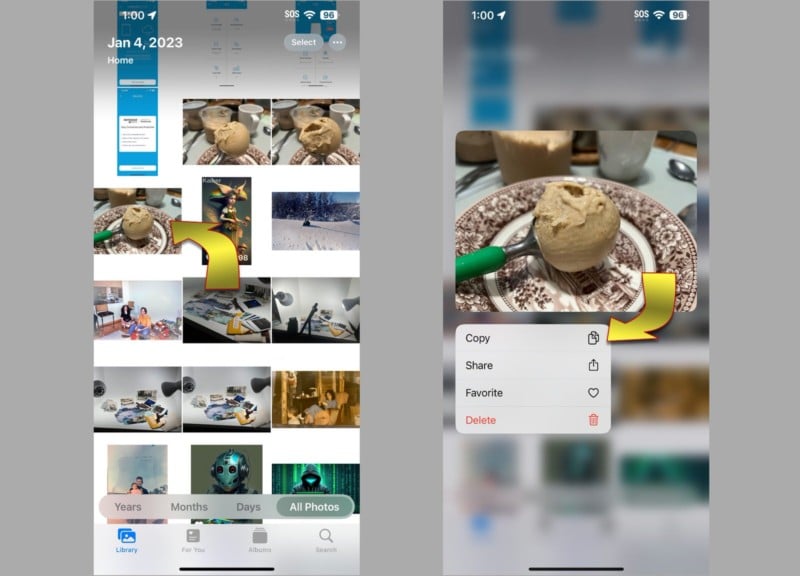
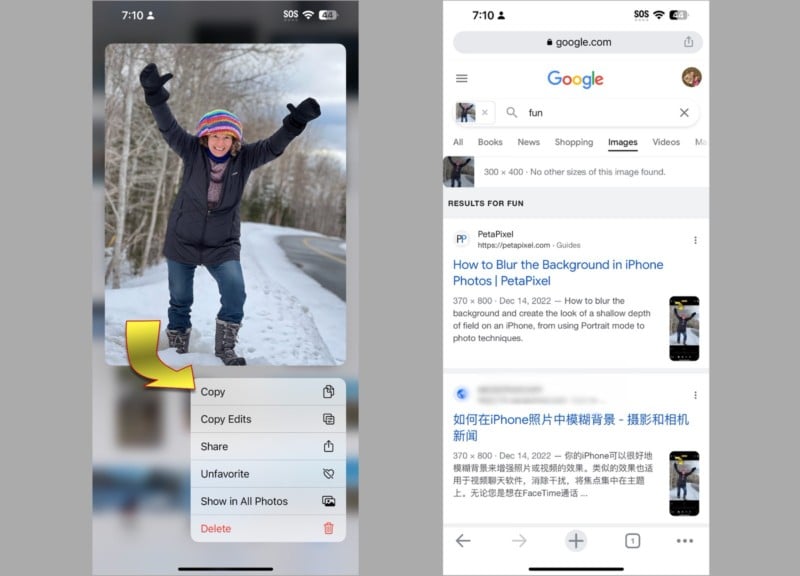
If you install the Google Chrome browser on your iPhone, a true reverse image search is possible. Start by finding the source picture in the Photos app, press and hold until the Share menu appears, and choose Copy.
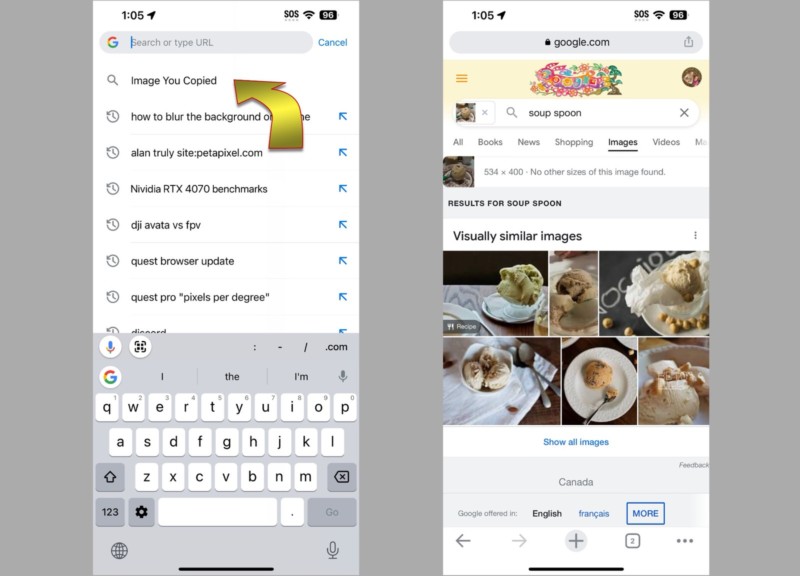
Then open Chrome and tap the search bar. At the top of the search suggestions list, select Image You Copied. Google will show related images and also fill in the search bar with what it thinks the search image is about.
If Google’s AI doesn’t identify the image correctly or if you want to refine the results, you can type your own keywords to see images that look similar and that also match the keywords you’ve supplied.
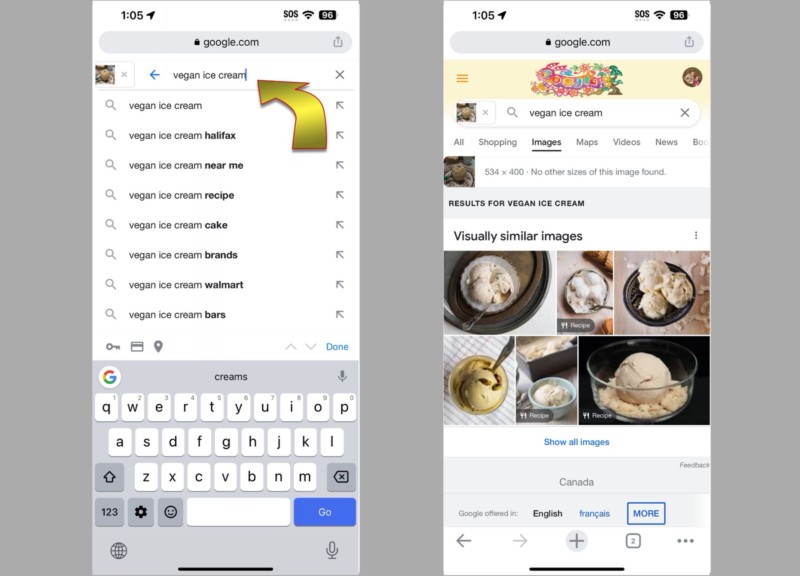
You can also search for an online image using keywords, then find related pictures by selecting the viewfinder icon that appears in the bottom-left of the image. This works the same in Google Chrome as it does in Apple’s Safari browser.
Bing’s Reverse Image Search
Microsoft is Google’s top search engine competitor and Bing has a visual search feature that works in a way that’s quite similar to Google’s reverse image search. You can access it via the Bing search engine in Safari, Chrome, or any other iPhone browser by tapping the viewfinder icon that’s in the search bar at the right. A camera preview will open so you can frame the object of interest. Hit the search button at the bottom to search for related images with Bing.
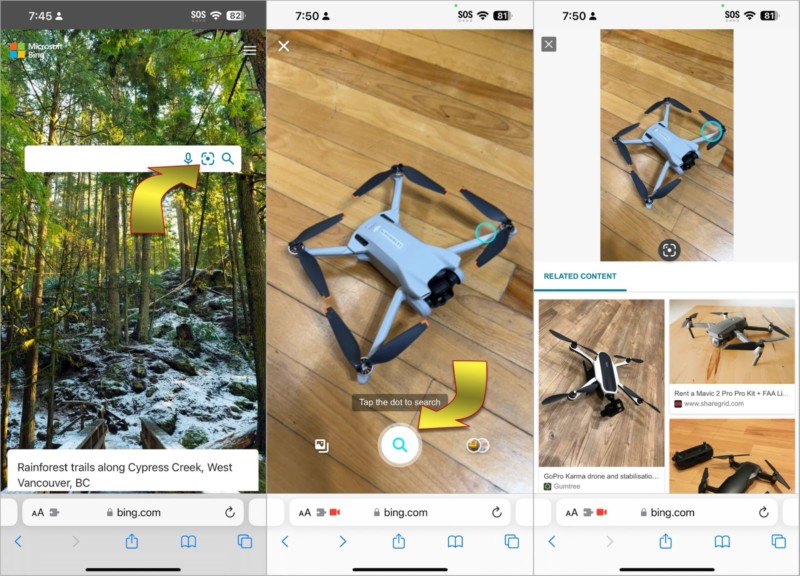
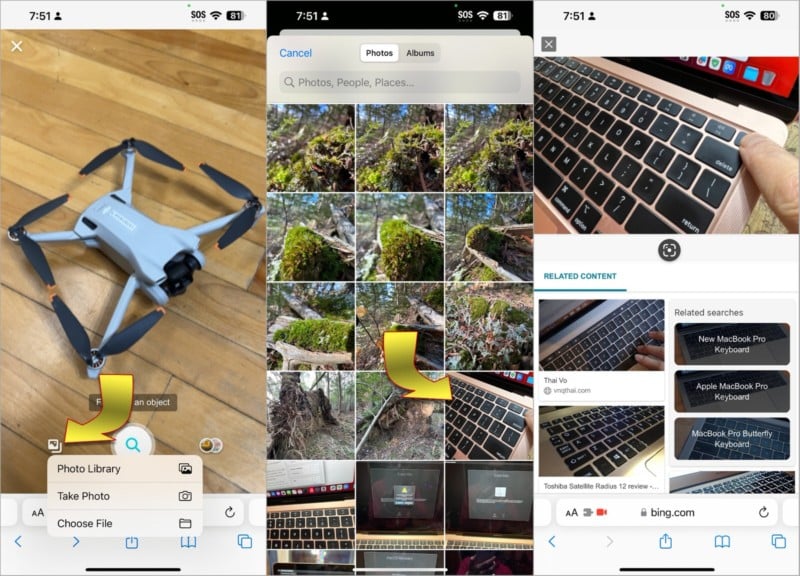
Bing also allows you to search for online visual matches of photos in your iPhone library. Tap the photos icon to the left of the search button, then Choose Photo Library to select a picture from your gallery or Choose File to browse for image files. After selecting a picture, Bing will search for related images.
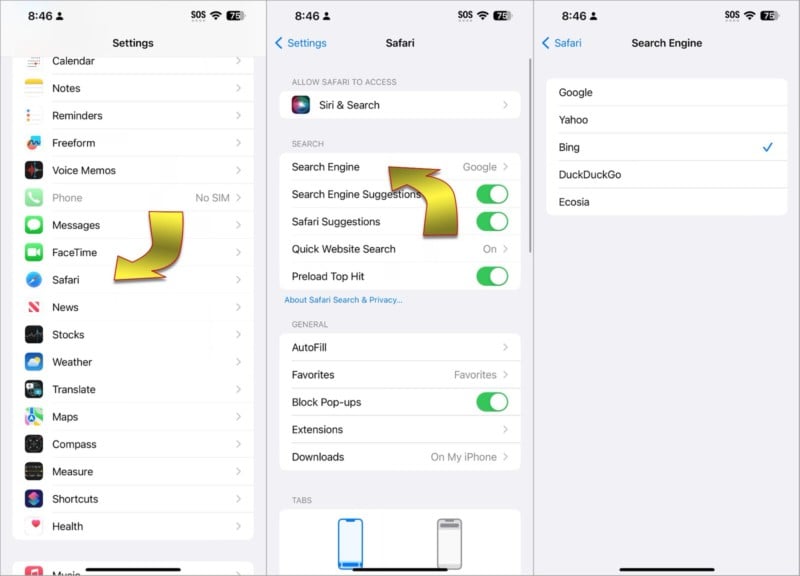
If you prefer using Bing or any other search engine instead of Google, changing the iPhone’s default setting is simple. Just open the Settings app, scroll down, and select Safari to see browser options. Near the top of that screen tap the control labeled Search Engine, then select your preferred source.
If you do a keyword search with Bing, switch to the images tab, and select a thumbnail, you’ll see the viewfinder icon below the image. Tap the viewfinder to find out what Bing thinks the subject looks like. Scroll down a little to see related content with similar images.
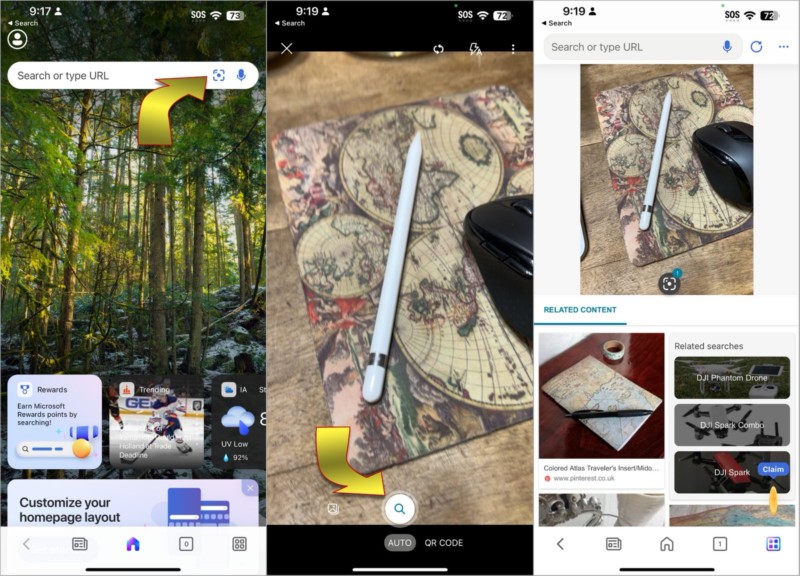
Bing nearly matches Google’s reverse image search, but it doesn’t offer a way to refine the results with keywords. Bing also has an iPhone app but it doesn’t add any extra image search features.
Uses for Reverse Image Search
There are many different uses for reverse image search. For example, you might want to check where your photos are being used online and a search for related content should place exact and very close matches at the top of the search. If the results are unexpected, it could be a case of copyright infringement.
It’s also possible to find matching patterns and colors for inspiration or to buy matching home decor such as wallpaper or fabric designs. Suppose you’ve taken a photo of a bird, plant, or insect, and want to add a caption but can’t identify it. In that case, a reverse image search can be beneficial in discovering its family and possibly finding the exact species.
Here are some of the main reasons to use a reverse image search engine:
- Tracking usage of your own images: If you are a photographer or any other kind of visual artist and own the copyright to images you’ve created, you can use a reverse image search engine to track how your image is being used online. If you find unauthorized uses, you can then consider working to end the usage and/or receive compensation for the infringement.
- Finding the source of an image: A reverse image search engine can help you find where an image originally came from or who is using it. Images on the internet are often shared without attribution, and reverse image searches can reveal where things were originally published.
- Checking image authenticity: It can help verify the authenticity of an image, especially when it comes to news, to ensure that the image is not fake or manipulated. A copy can be compared to the original source for an image to reveal any possible changes that had been added since the original publication.
- Finding similar images: It can help you find similar images to a particular picture, which can be useful for finding different perspectives or variations of the same subject. If you are looking for inspiration or collecting images for something like a mood board, reverse searching can help you quickly find images with the same subject, style, and aesthetics.
- Identifying objects or landmarks: If you have a picture of an object or landmark and want to know more about it, a reverse image search engine can help you find information. Search engines can use powerful AI recognition technologies to quickly identify everything from a mushroom you come across to a particular work of art.
Conclusion
Machine learning has taken huge steps in making image processing much more useful. While its use in refining photographs and creating has been making headlines recently, reverse image search might be even more valuable in helping to identify content and find visual matches within an online library of hundreds of billions of pictures. This process might otherwise take a lifetime without the help of Google, Bing, and other visual search engine providers.